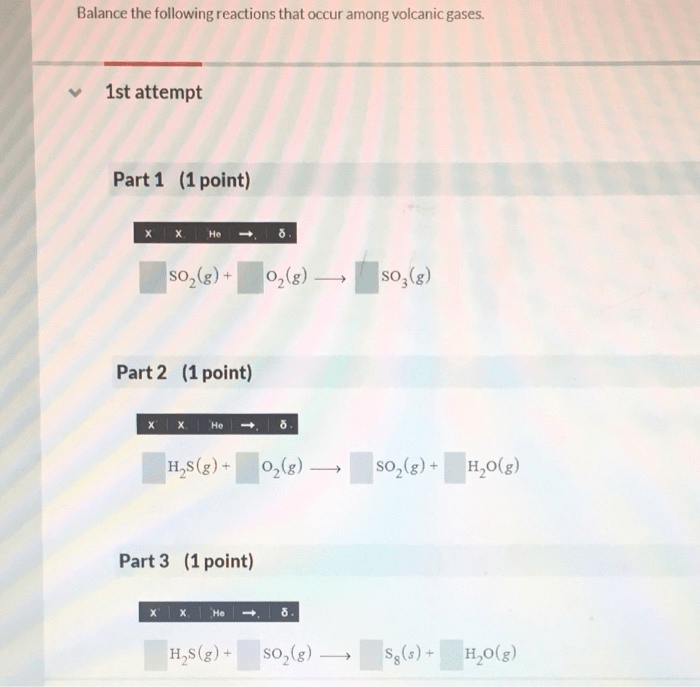
Balance the following reactions that occur among volcanic gases. Volcanic gases play a crucial role in shaping volcanic processes and understanding their behavior. This article delves into the chemical reactions involving these gases, exploring their significance and the factors that influence their interactions.
Delving into the intricacies of volcanic gas reactions, we uncover the principles of balancing chemical equations and apply them specifically to volcanic gas reactions. A comprehensive table presents balanced reactions for common volcanic gases, providing a valuable resource for further study.
Chemical Reactions of Volcanic Gases
Volcanic gases are a mixture of gases released from volcanoes during volcanic eruptions. These gases can include water vapor, carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, hydrogen chloride, and other trace gases. The chemical reactions that occur among these gases can have a significant impact on the composition of the volcanic plume and the surrounding environment.
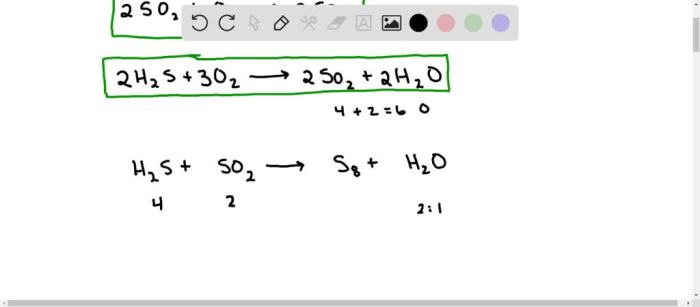
One of the most common reactions that occurs among volcanic gases is the oxidation of sulfur dioxide to form sulfur trioxide. This reaction is catalyzed by water vapor and can be represented by the following equation:
2 SO2+ O 2+ 2 H 2O → 2 H 2SO 4
This reaction can produce sulfuric acid aerosols, which can contribute to acid rain and have a negative impact on air quality and human health.
Another common reaction that occurs among volcanic gases is the formation of hydrogen chloride from the reaction of hydrogen sulfide with chlorine. This reaction can be represented by the following equation:
H2S + Cl 2→ 2 HCl + S
Hydrogen chloride is a corrosive gas that can irritate the eyes, nose, and throat. It can also contribute to the formation of acid rain.
Balancing Volcanic Gas Reactions
Balancing chemical reactions is essential for understanding the stoichiometry of the reaction and predicting the products that will be formed. To balance a chemical reaction, the number of atoms of each element must be the same on both sides of the equation.
To balance a reaction involving volcanic gases, the following steps can be followed:
- Write the unbalanced equation.
- Identify the element that is unbalanced.
- Add coefficients to the reactants and products to balance the number of atoms of the unbalanced element.
- Repeat steps 2 and 3 for each unbalanced element until the equation is balanced.
For example, the following unbalanced equation can be balanced by adding coefficients to the reactants and products:
2 SO2+ O 2+ 2 H 2O → 2 H 2SO 4
The balanced equation is:
2 SO2+ O 2+ 2 H 2O → 2 H 2SO 4
Factors Affecting Volcanic Gas Reactions
The reactions that occur among volcanic gases can be affected by a number of factors, including temperature, pressure, and the presence of other gases.
Temperature can affect the rate of reaction and the products that are formed. For example, the oxidation of sulfur dioxide to sulfur trioxide is more likely to occur at higher temperatures. Pressure can also affect the rate of reaction and the products that are formed.
For example, the formation of hydrogen chloride from the reaction of hydrogen sulfide with chlorine is more likely to occur at higher pressures.
The presence of other gases can also affect the reactions that occur among volcanic gases. For example, the presence of water vapor can catalyze the oxidation of sulfur dioxide to sulfur trioxide. The presence of chlorine can also promote the formation of hydrogen chloride from the reaction of hydrogen sulfide with chlorine.
Significance of Volcanic Gas Reactions

The reactions that occur among volcanic gases can have a significant impact on volcanic processes and the surrounding environment. These reactions can produce gases that are harmful to human health and the environment, and they can also contribute to the formation of acid rain.
The reactions that occur among volcanic gases can also provide insights into the composition of the Earth’s interior and the processes that occur within volcanoes. By studying these reactions, scientists can gain a better understanding of volcanic processes and the potential hazards that they pose.
Clarifying Questions: Balance The Following Reactions That Occur Among Volcanic Gases
What are the common volcanic gases?
Common volcanic gases include water vapor, carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, and hydrogen chloride.
How do temperature and pressure affect volcanic gas reactions?
Temperature and pressure can significantly influence the rates and products of volcanic gas reactions. Higher temperatures generally favor reactions that produce more stable products, while higher pressures shift the equilibrium towards reactions that produce fewer moles of gas.
What are the hazards associated with volcanic gas emissions?
Volcanic gas emissions can pose hazards to human health and the environment. Sulfur dioxide can cause respiratory problems, while hydrogen sulfide is toxic and can be fatal in high concentrations. Volcanic gases can also contribute to acid rain and climate change.